
Meet Zoom AI Companion, your new AI assistant!
Boost productivity and team collaboration with Zoom AI Companion, available at no additional cost with eligible paid Zoom plans.
Updated on October 09, 2025
Published on October 09, 2025


Think of business communication as your company’s hidden operating system. When it’s running smoothly, everything works as you want it to. But when it breaks down — like when a colleague or customer misses or misunderstands a message — the company misses its deadlines, clients lose confidence in you, and you have to spend time and resources fixing it.
Communication is the thread that connects people, decisions, and outcomes. Get it right, and it improves everything from the customer experience to investor confidence. Business leaders agree: 64% say it increases productivity, boosts customer satisfaction, and raises employee confidence, according to a Grammarly report.
In this article, we’ll discuss what business communication is, why it’s distinct from other types of communication, and how to get better at it.
Business communication is the exchange of information or ideas — typically via speaking, writing, or an audiovisual component — in a business context. For example, sending your coworker an instant message via Zoom Team Chat to remind them of an upcoming deadline is business communication in action.
Communication in the workplace presents unique challenges and often higher risks than, say, a conversation with the cashier at the grocery store. The cost of miscommunication can be high — up to $12,506 per employee per year. However, the rewards of good communication are often proportionally high.

The importance of good business communication is perhaps obvious: Without clear and efficient communication, you can’t provide the products and services your customers know and love. This concept may seem simple, but to succeed at work, it’s critical to understand how business communication differs from other types of day-to-day communication.
Good communication helps make your operations more efficient, strengthen your internal and external relationships, and improve brand reputation.
Bad communication can lead to missed deadlines, strained relationships between clients and coworkers, and incoherent processes that cost your team time and money.
Incidentally, this is one of the biggest discussions around implementing artificial intelligence (AI). AI adoption can increase efficiency and productivity, but when it comes to communication, AI can struggle to provide a personal touch.
We don’t think (at least consciously) about communication often — but that’s because we do it all the time. And like many things we do all the time and don’t think about, sometimes it’s essential to go back to those processes and habits and make sure we’re doing them the right way.
We generally divide business communication into two types: internal and external. Each has its own quirks, and understanding both is necessary for effective communication in the workplace.
Internal communication is communication within your organization, focused mainly on achieving company goals and maintaining company culture. External communication is how you interact with customers, shareholders, and others outside your organization.
Let’s look at some business communication examples for each type.
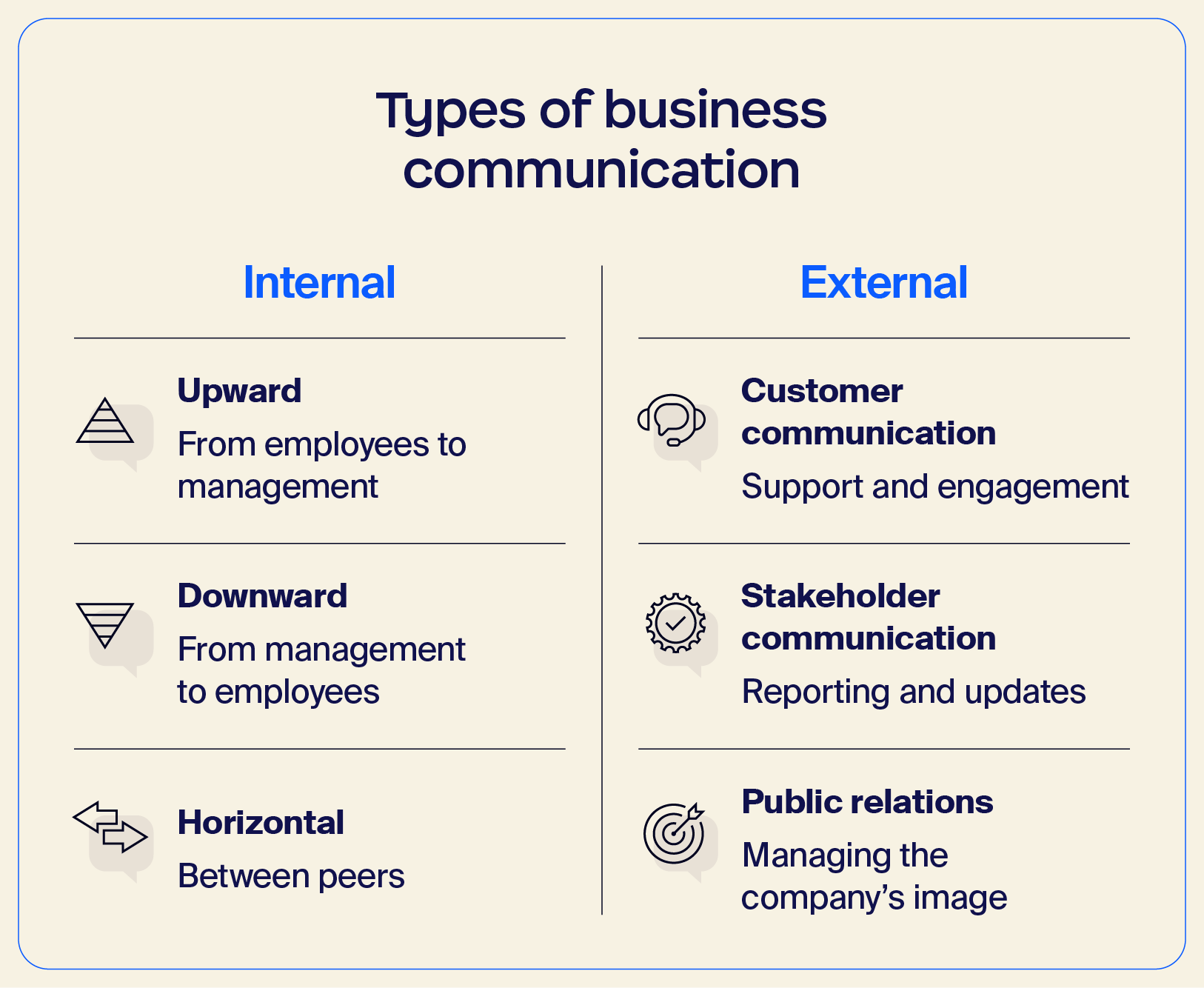
Upward internal communication involves the flow of information from employees to management. When employees provide feedback, report issues, or share ideas, that’s upward internal communication in action.
Pros:
Cons:
Example: A sales team employee identifies a recurring customer complaint and submits a suggestion box entry proposing a solution to the product development team. This suggestion is then used to improve the product and ultimately helps the sales team close more deals.
Tip: Maintain an open-door policy to create a safe and supportive environment for employees to share their experiences without fear of consequences.
Downward communication occurs when information flows from management to employees. This usually involves providing instructions, goals, expectations, or insight about the company’s direction.
Some pros and cons of downward communication include:
Pros:
Cons:
Example: A manager sends a department email detailing upcoming project deadlines, task assignments, and team goals. This gives all employees a clear idea of upcoming projects and expectations.
Tip: Establish regular feedback mechanisms or opportunities so that employees can ask questions and provide feedback on instructions and goals provided by managers. This helps facilitate a meaningful two-way dialogue between employees and managers.
Horizontal communication, sometimes called lateral communication, is all communication between peers. This type of communication can happen across departments as long as all parties are at the same organizational level.
Some pros and cons of horizontal communication include:
Pros:
Cons:
Example: An engineer from the product development team consults with the design team to align a new feature with user experience best practices. This individual then creates a more optimized product for the end user.
Tip: Establish transparent processes for requesting and receiving horizontal feedback and collaborating across teams. The more transparent you can make these clear channels and processes, the better! This will make relevant information available to all stakeholders and keep managers in the loop.

Customer communication may be the first thing that comes to mind when looking for an example of business communication. This often involves solving customer problems with the product or service, troubleshooting, managing customer relationships, and more.
Some pros and cons of customer communication include:
Pros:
Cons:
Example: A company might create a knowledge base of frequently asked questions (FAQs) and troubleshooting guides on its website to help customers find solutions independently.
Tip: An omnichannel contact center experience can streamline customer communication and help your team provide highly personalized responses.
Stakeholder communication is similar to upward communication but takes place outside the company. It can involve sharing company updates with investors, suppliers, or the wider community.
Some pros and cons of stakeholder communication include:
Pros:
Cons:
Example: A company might report a successful year to investors by providing a list of achievements, such as 15% revenue growth, improved profit margins, and/or expansion plans.
Tip: Tailor all communications with stakeholders to each group’s interests, providing the most relevant information for further understanding your company.
Finally, public relations (PR) involves sharing information from a company like yours with the public. This process usually involves shaping and maintaining a particular narrative or image to build a relationship with the audience.
Some pros and cons of public relations include:
Pros:
Cons:
Example: A company proactively issues a press release to address a negative news story, clarifying the situation and taking responsibility for any shortcomings.
Tip: Stay engaged with your audience through multiple channels, including social media, press releases, and events. Staying connected with your audience helps build a positive presence in the community.
Now that we’ve covered the different types of communication, let’s talk about how to reach your audience with each kind of business communication. These are some of the most common business communication channels — most of which you’ve probably used at one point or another:
Internally, email is one type of business communication solution for sending managerial communications like upcoming shift patterns as well as important news and announcements.
Externally, email is the prime way to distribute documents among stakeholders, reach out to media and PR contacts, and send marketing campaigns to new and existing customers.
Instant messaging channels like iMessage or WhatsApp are excellent quick response channels for handling sales and customer service inquiries from customers.
Internally, instant messaging via business communication software like Slack or Zoom Team Chat is highly effective at facilitating real-time collaboration between team members and departments.
Internally, leading video conferencing use cases include hosting virtual meetings, running remote training, and collaborative work that requires screen sharing.
Externally, they’re ideal for sales meetings, live product demos, and support calls where face-to-face interaction helps agents explain solutions more effectively to customers.
Project management tools are useful for coordinating product development and guiding sales teams through longer, more complex sales cycles.
For external communication, they’re great if you’re involving third-party contractors or clients in a project to show them progress and gain their feedback.
Social media is an excellent tool for one-on-one interactions with customers as well as brand building, marketing, and customer service. It creates a direct, authentic way for brands to communicate with their user base on their personal terms.
| Want to help your team write better? Find out how Zoom’s AI writing tools improve productivity and help teams better shape their communication with colleagues and customers. |
Building efficient and effective business communication skills and practices is essential to building and maintaining a successful business. After all, if you can’t communicate effectively, all parts of your business will be less efficient than they could be.
With this in mind, we’ll look at five ways to improve communication within your operation.
Setting clear expectations and goals for your team makes prioritizing easier across the board. By establishing clear objectives (and prioritizing problem areas), you can better track progress and make informed project adjustments as needed.
A good communication process will struggle without comprehensive business communication training. Make sure to train all team members in the communication expectations for their roles and responsibilities.
To help your employees to communicate effectively, invest in technology like Zoom Meetings to keep everyone connected and on the same page. Video meetings and team chats centralize communication and make feedback and collaboration easy.
Communication processes are rarely just set-it-and-forget-it. Encourage employees to give feedback on both internal and external communication processes to improve continuously. A transparent review process and open-door policies can go a long way in achieving this goal.
Finally, keep an eye on the success of your communication processes. Is information being distributed successfully? Is anyone confused? Are there regular moments of misunderstanding or need for clarification?
Pinpointing these moments can help you identify where you need to adjust your business communication processes.
We’ve covered the types of communication in business and some common use cases; now we’ll go over practical applications. These tools can help your team do more — and do it more efficiently!
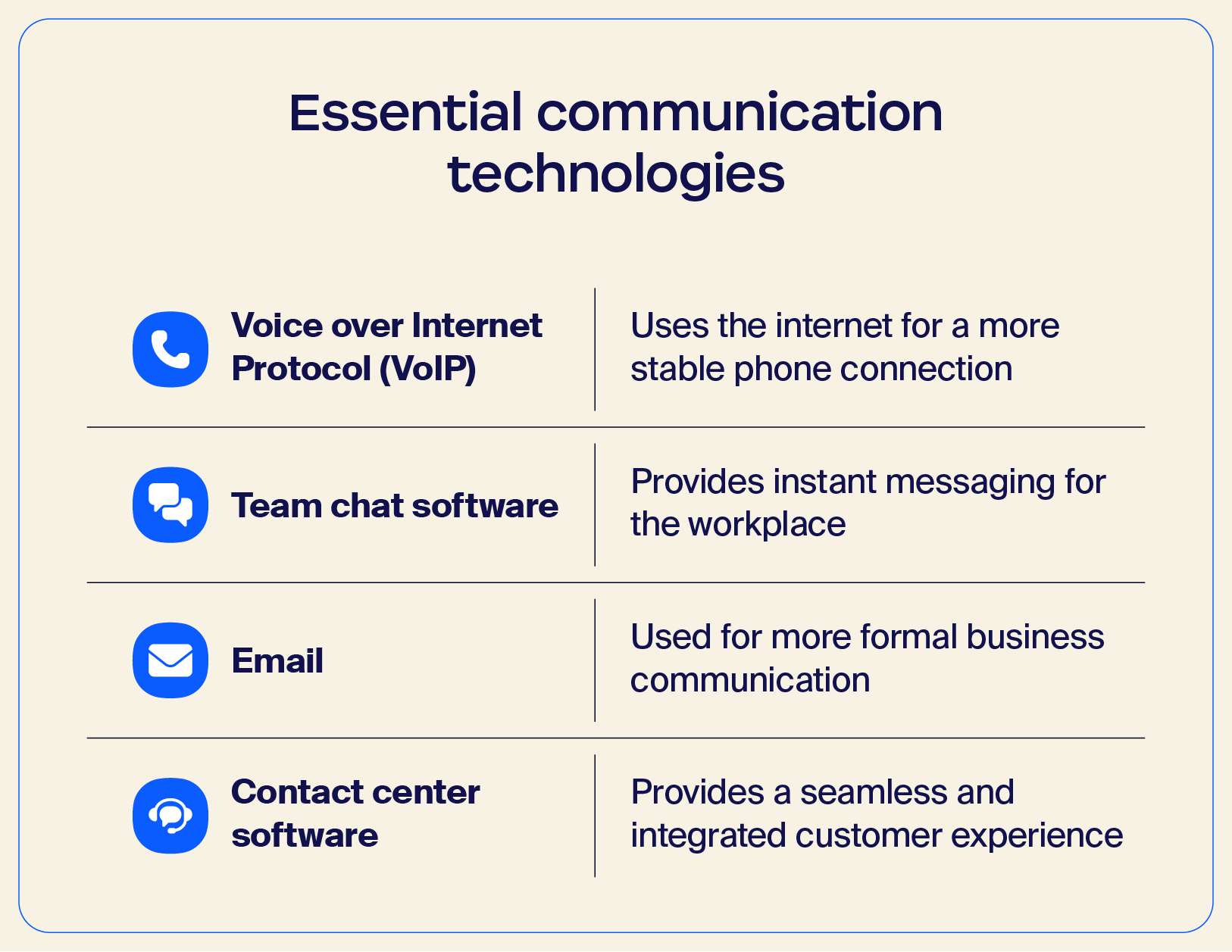
How it can help: Allows for cost-effective communication with customers, co-workers, and partners anywhere in the world
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is a tool that makes international business calls simple and easy. It functions just like a regular telephone but uses the internet to reach the other person on the line. This technology uses an internet connection instead of traditional phone lines, which can help your team communicate globally.
You can now add AI-powered features to many cloud VoIP packages, such as note-taking, SMS capabilities, and call summaries.
How it can help: Enables quick, informal team collaboration and fast problem-solving
Team chat software is indispensable to business communication in the modern workplace. Instant messaging through team chat is faster and often more efficient than email, allowing quick and easy communication with teammates and supervisors.
How it can help: Great for sending quotes, conveying information, and distributing documents
We all know and love the power of email for professional communication. But did you know you can do more with email than ever before? Zoom Mail Service offers end-to-end encryption, easy appointment scheduling, and customizable domains, all within the mail client.
How it can help: Manages incoming calls, texts, social media chat, chatbot conversations, and text messaging
Finally, a contact center software tool is essential to customer-facing communication today. When considering the customer’s preferences as part of an ideal customer experience, an integrated video-based contact center just makes sense.
Check out this checklist to see if your business could benefit from a cloud-based contact center solution.
If you feel inspired by these business communication examples and are ready to examine your processes again, we hope this overview of the available technologies and tools will help you optimize for success. Communication is a critical part of business operations — and the tools necessary to facilitate good communication are just as critical.
Ready to take the next step toward a more collaborative workplace? Bring your team together with virtual video conferencing from Zoom.