
Meet Zoom AI Companion, your new AI assistant!
Boost productivity and team collaboration with Zoom AI Companion, available at no additional cost with eligible paid Zoom plans.
Updated on February 28, 2025
Published on February 28, 2025

In the fast-paced world of contact centers, managing high call volumes while delivering exceptional customer service is no small feat. Agents often start calls with limited information, which can lead to longer handling times and customer frustration. This is where automatic number identification (ANI) makes a difference.
ANI identifies the caller’s phone number so that an agent doesn’t have to spend time trying to identify them. Instead, they can start the call with all the background information and customer history associated with that phone number. Contact centers use this information to identify callers, pull up relevant records, and route calls more efficiently, reducing wait times and enhancing the overall experience.
Automatic number identification is a telecommunications feature that automatically captures and transmits the phone number of an incoming caller to the recipient. While it’s often compared to caller ID, ANI is a more sophisticated technology that provides the phone number through the network signaling system — a more reliable method even in cases where caller ID might be blocked or unavailable.
ANI enables agents to access relevant customer data before answering the call. This helps reduce the time spent gathering basic information, allowing agents to focus on resolving the issue at hand more efficiently. Additionally, ANI is often used to route calls based on the caller’s location or previous interactions, creating a more personalized and seamless customer experience.
For businesses handling high call volumes, ANI provides insights that are helpful for streamlining workflows. It enables automated systems to verify caller identities, flag potential fraud, like spam and automated calls, and prioritize certain customers based on predefined criteria. These capabilities make ANI a practical choice for improving contact center efficiency and supporting better service delivery.
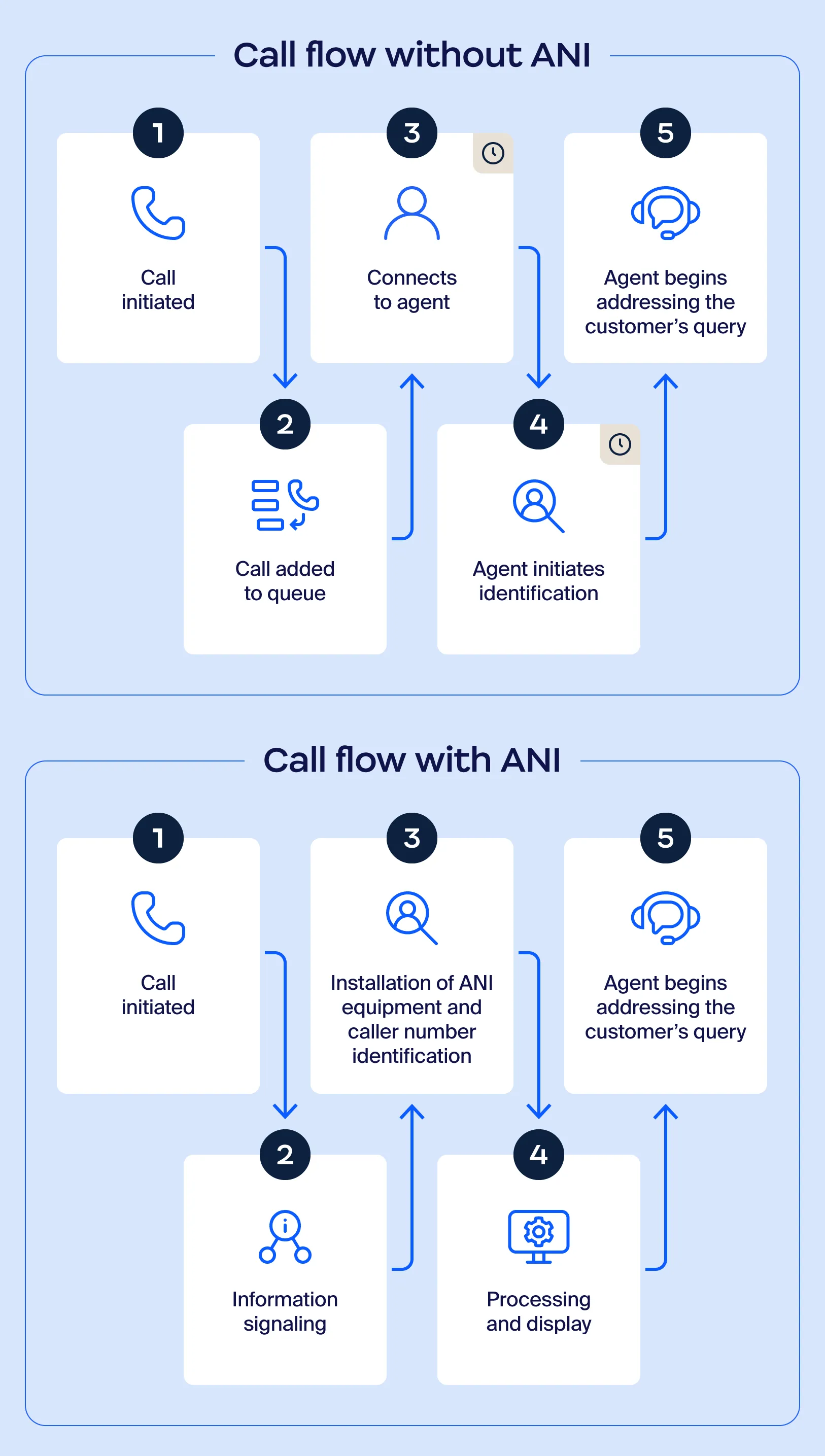
In contact centers, automatic number identification functions by capturing the caller’s phone number and transmitting it to the recipient via the telecommunication signaling system.
When a call is placed, it doesn’t just travel directly from one phone to another. Behind the scenes, a signaling system handles the technical steps of routing the call through the network. It sends the caller’s phone number and other data through separate channels so the information reaches its destination even before the recipient answers the call.
This means the caller’s number is still available to the recipient’s network, even if caller ID is blocked.
Once received, ANI data is integrated with the contact center’s customer relationship management (CRM) or call management systems. This allows agents to instantly access customer profiles, transaction history, or other relevant details, reducing the time spent gathering basic information. Additionally, ANI is often paired with automated routing systems to direct calls to the appropriate department or agent based on predefined rules, such as geographic location, customer status, or previous interactions.
Although dialed number identification service (DNIS), ANI, and caller ID all deal with call-related information, they serve distinct purposes within the telecommunications and contact center ecosystem. Understanding these differences can help businesses determine how to utilize each feature best.
Together, these tools can enhance contact center operations, but ANI and DNIS stand out for their utility in high-volume, professional environments.
Automatic number identification offers several advantages that help contact centers improve efficiency, customer interactions, and overall operations. Here’s what ANI can help you do:
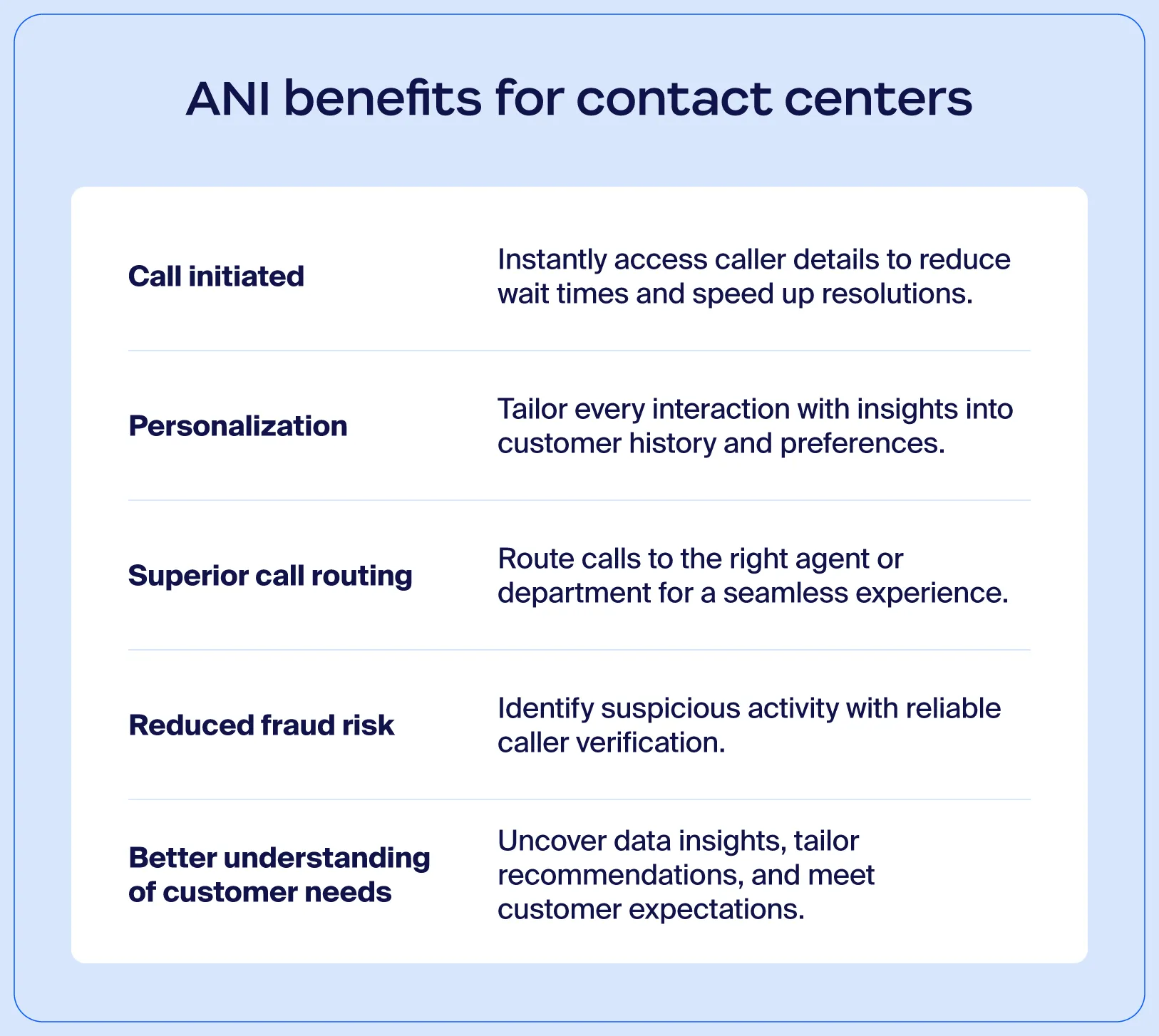
A personalized experience is just as important as excellent audio quality and a hiccup-free customer journey. Customers feel valued when agents know who they are and what they need, leading to a more positive impression of the business.
Since ANI enables contact centers to recognize customers as soon as they call, agents can greet them by name and access relevant account or interaction histories immediately. This eliminates the need for repetitive questions, such as asking for account numbers or prior interactions, and creates a smoother and more personalized experience.
With ANI, agents no longer need to manually verify caller information, such as account numbers or other identifiers. The caller’s number is automatically matched with the contact center’s database, pulling up their records in real time. This not only saves time but also allows agents to focus on resolving issues more quickly. For high-volume call centers, this benefit can translate into shorter wait times and increased efficiency.
ANI can be integrated with automated call distribution systems to route calls more effectively. For example, calls can be directed to specific departments or agents based on the caller’s location, account status, or previous interactions. This reduces misrouting and helps direct customers so that they’re connected to the right person the first time.
Better routing means fewer transfers, shorter call times, and higher first-call resolution rates, which are important for maintaining high customer satisfaction levels.
ANI provides an added layer of security by verifying the caller’s number. Contact centers can flag suspicious or unrecognized numbers, reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access. This capability is particularly valuable for businesses in industries that handle sensitive information, like finance or healthcare.
For example, if someone tries to use your information to make changes to your account through customer support, agents can flag the unrecognized phone number and try to confirm the caller’s identity.
Because ANI pulls up customer details immediately, agents can tailor their interactions to the caller’s needs. This includes making personalized product or service recommendations based on the customer’s history, preferences, or past inquiries.
For example, if a customer previously inquired about an upgrade, the agent can proactively suggest options during the call. These personalized recommendations not only enhance the customer experience but also open opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Adding automatic number identification to your contact center software is a straightforward process that starts with evaluating your current telephony system and contact center solutions. Many modern contact center platforms already support ANI functionality, either natively or through integrations.
Check to see if your current provider offers ANI functionality. Otherwise, you’ll need to look into reliable and scalable service providers and compare functionalities to find the best fit for you. Once you’ve implemented ANI, you can connect it to your CRM system and call routing tools to unlock its full potential.
Ready to take your contact center to the next level with ANI? Zoom Contact Center offers robust ANI and call handling capabilities to help you streamline operations and elevate customer satisfaction. Reach out today to explore how our solutions can support your business goals and create a better customer experience.
Still have questions about automatic number identification? Here are answers to some of the most common queries to help you better understand how this technology works and its implications for your contact center.
ANI is a telecommunication feature primarily used by service providers to capture and transmit the caller’s phone number for billing and operational purposes. It provides reliable data that cannot be blocked by the caller.
Calling line identification (CLI), otherwise known as caller ID, is a feature designed for end users, such as businesses or individuals, to display the caller’s number on their phone or device. CLI data can be manipulated or withheld by the caller, making it less reliable in some cases.
ANI screening is a process that uses ANI data to identify and filter incoming calls based on predefined criteria. For example, businesses can use ANI screening to prioritize calls from premium customers, block known spam or fraudulent numbers, or route calls to specific departments based on the caller’s location.
While ANI provides valuable caller information, businesses must handle this data responsibly to protect customer privacy and comply with data protection regulations.
Most reputable contact center software providers incorporate robust security measures, such as encryption and data access controls, to safeguard ANI data. However, it’s important for businesses to work with providers who prioritize compliance with privacy laws like GDPR or CCPA and implement internal policies that limit access to sensitive data.