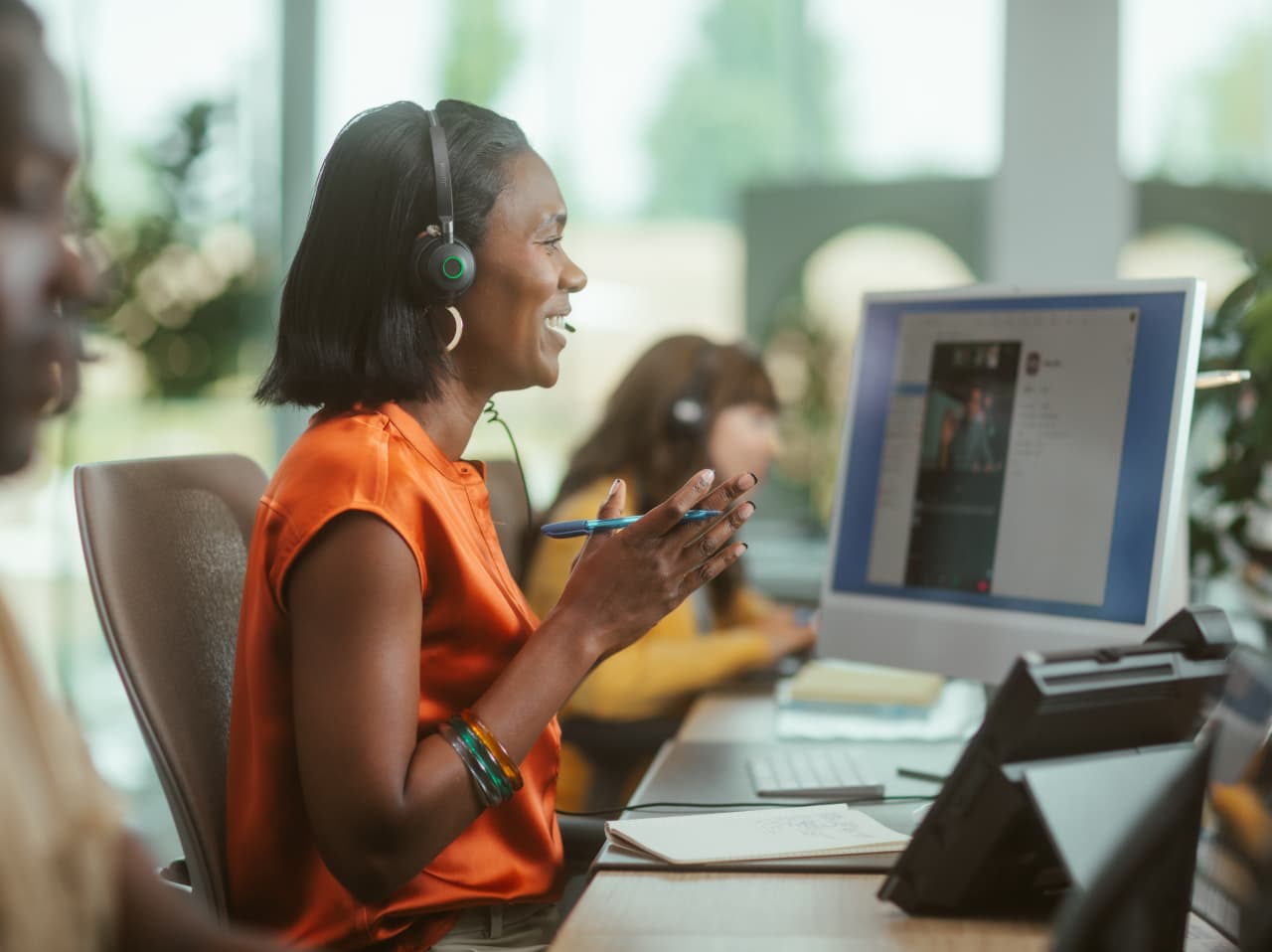
Skills-based routing (SBR) is a method used in contact centers to direct incoming consumer engagements to the most qualified agent based on specific skill sets. Unlike traditional routing systems that simply assign engagements based on availability (longest idle being a commonly used method), Skills Based Routing evaluates the nature of the consumer’s query and matches it to a set of agents with the right skills.
Some examples of skills may include:
- Language
-
Technical knowledge
-
Product specialization
This approach aims to improve the customer experience by having calls answered by an agent who is best positioned to deal with the customer's query without having to transfer to another member of the team. By doing this, issues can be resolved more quickly and accurately, contributing to higher efficiency, lower resolution times, improved overall service quality, and first-contact resolution.
There are four key components that we need to consider when building a Skills Based Routing setup.
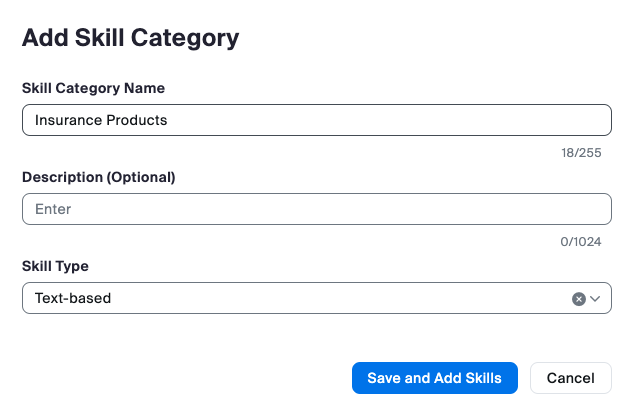
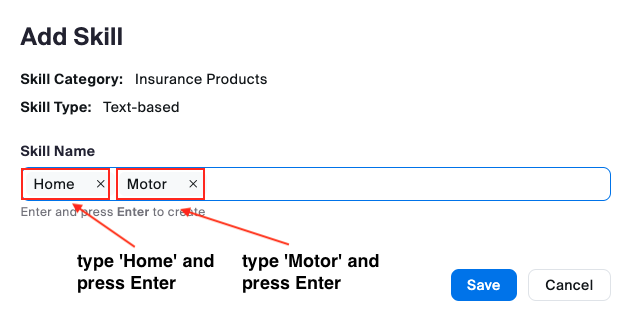
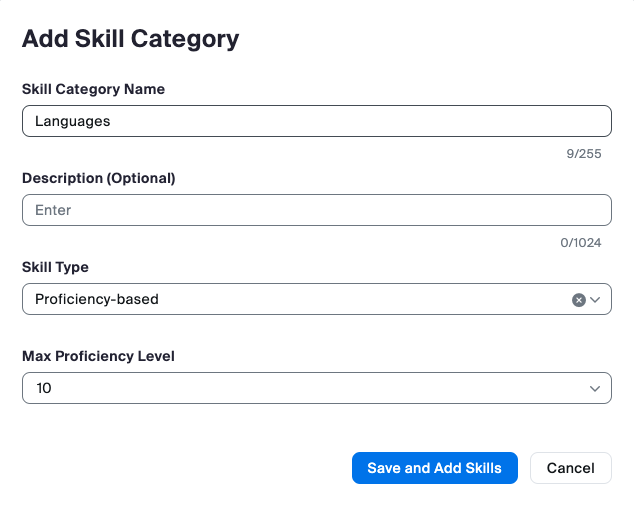
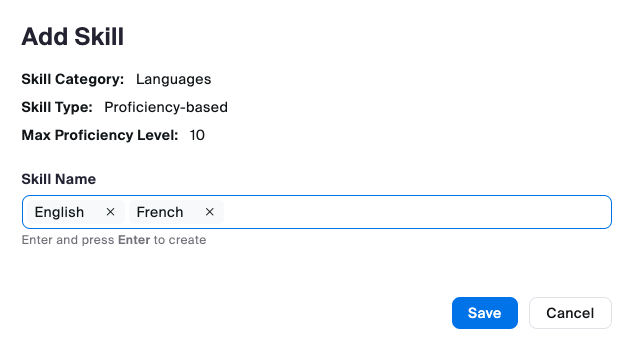
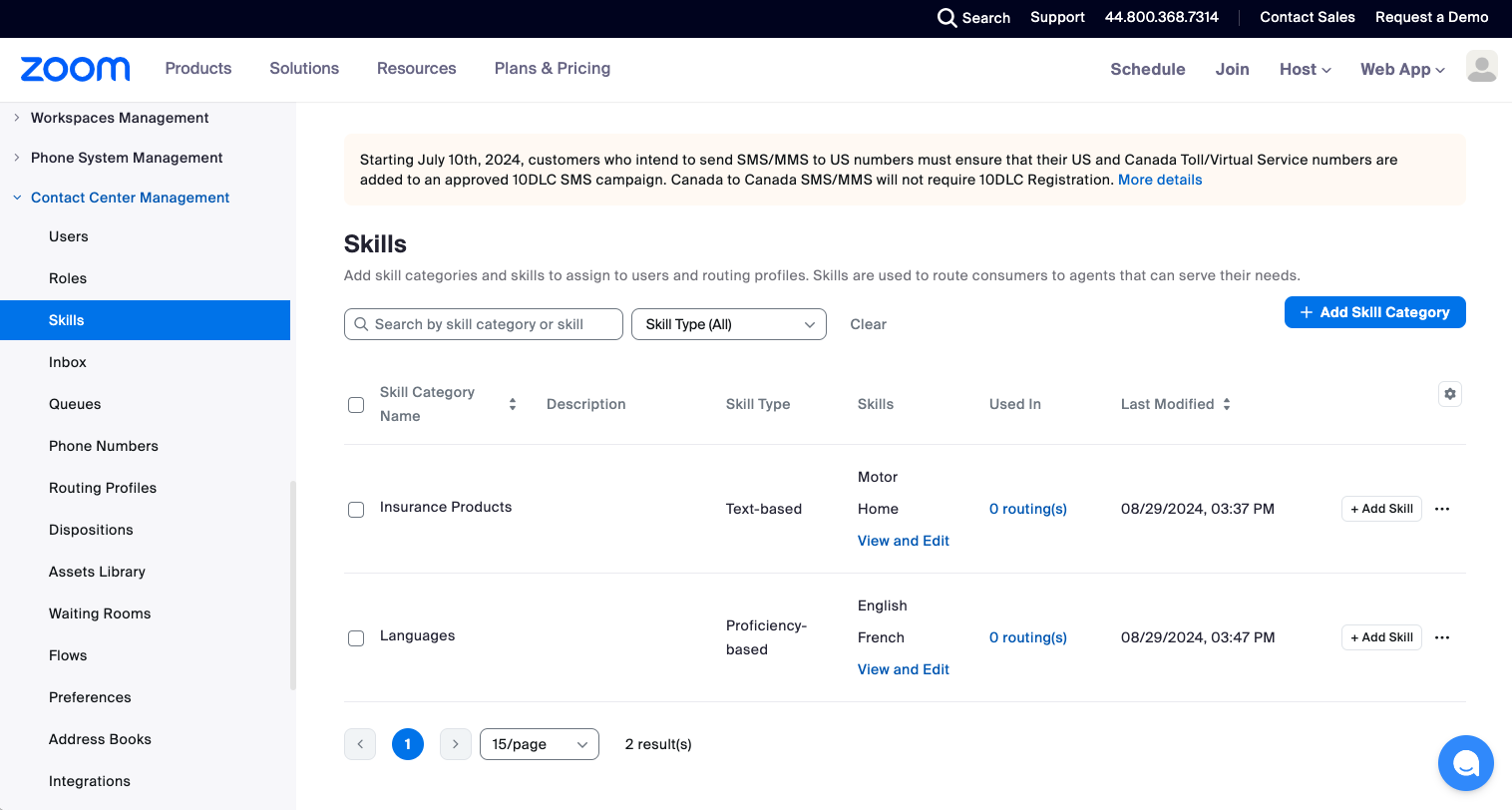
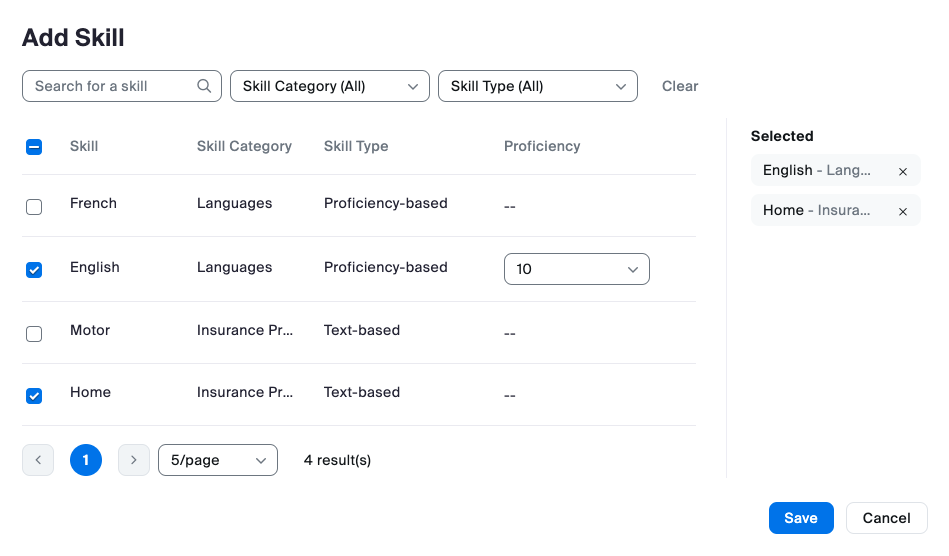
Skills & Skill Categories:
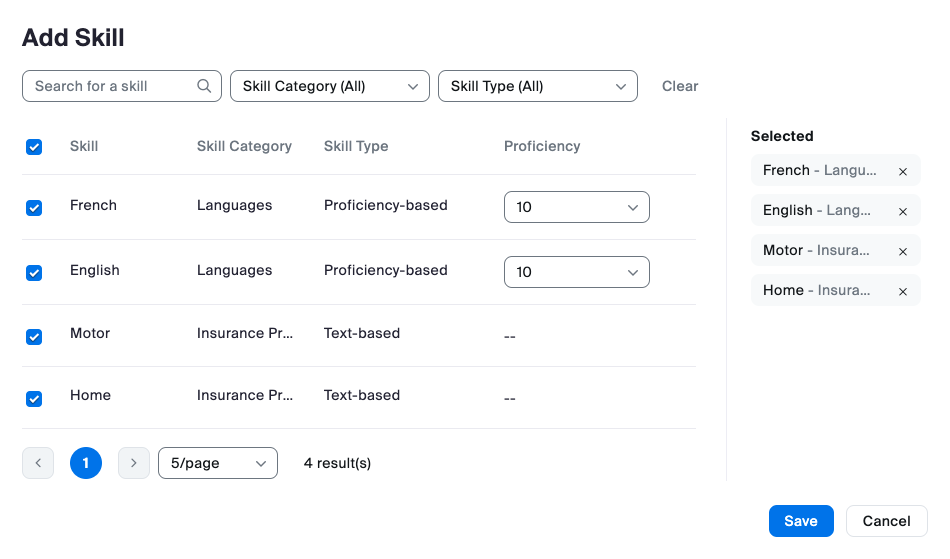
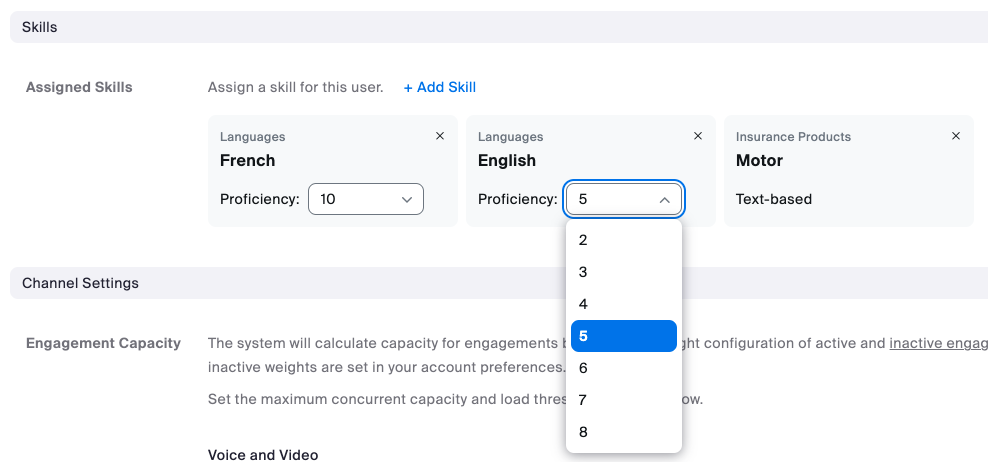
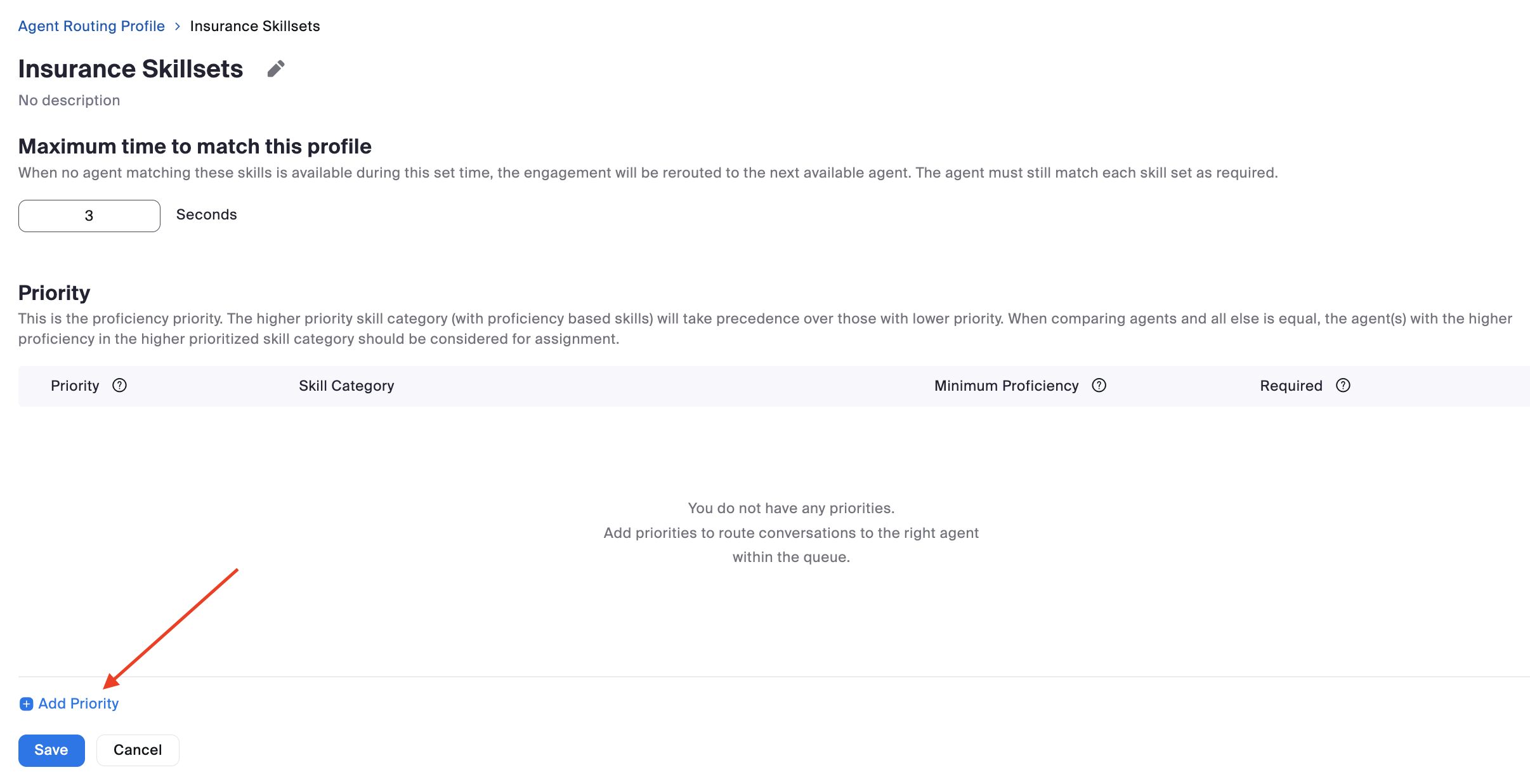
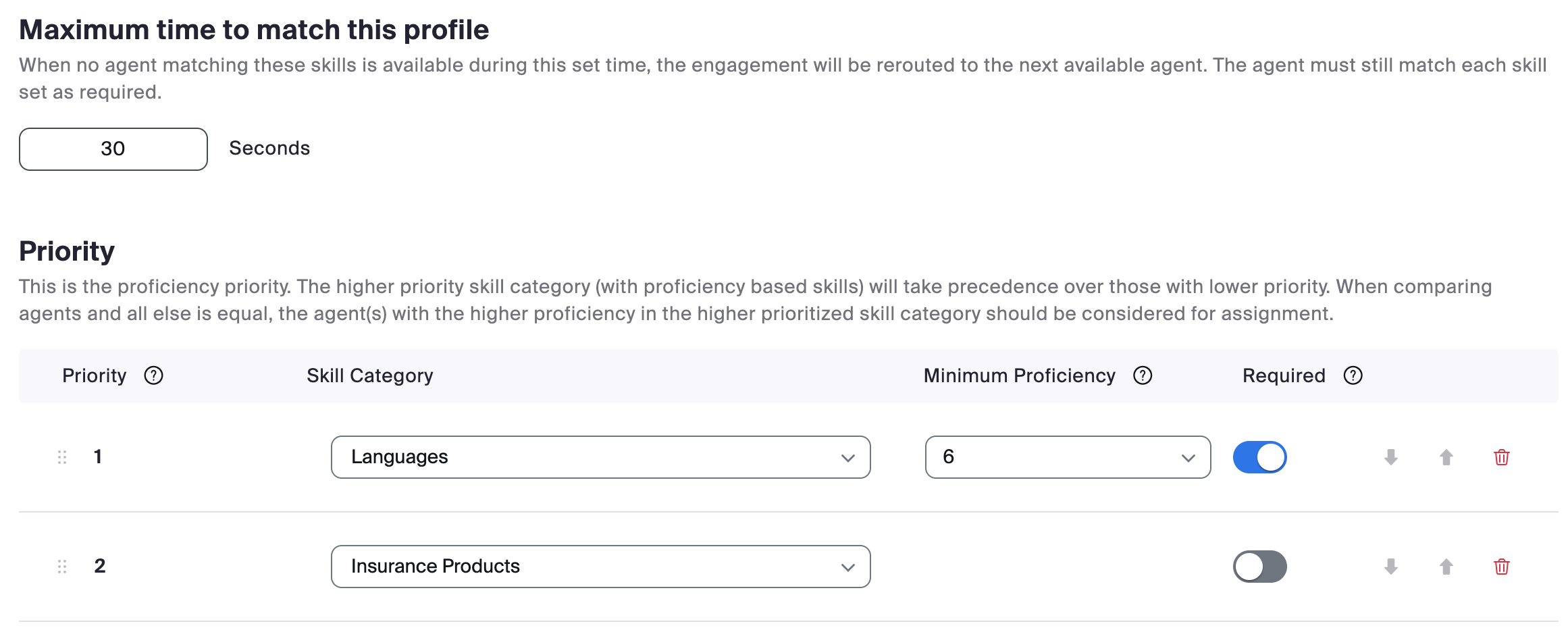
Skills are agent traits that indicate that they are the right person to handle a customer interaction. Proficiency ratings correspond to the agent’s level of expertise or knowledge of that skill. Skills are assigned to agents' profiles to define which skills they possess and, optionally, their proficiency in that particular set of skills. A higher proficiency rating means an agent is better at that skill.
Agent Routing Profiles :
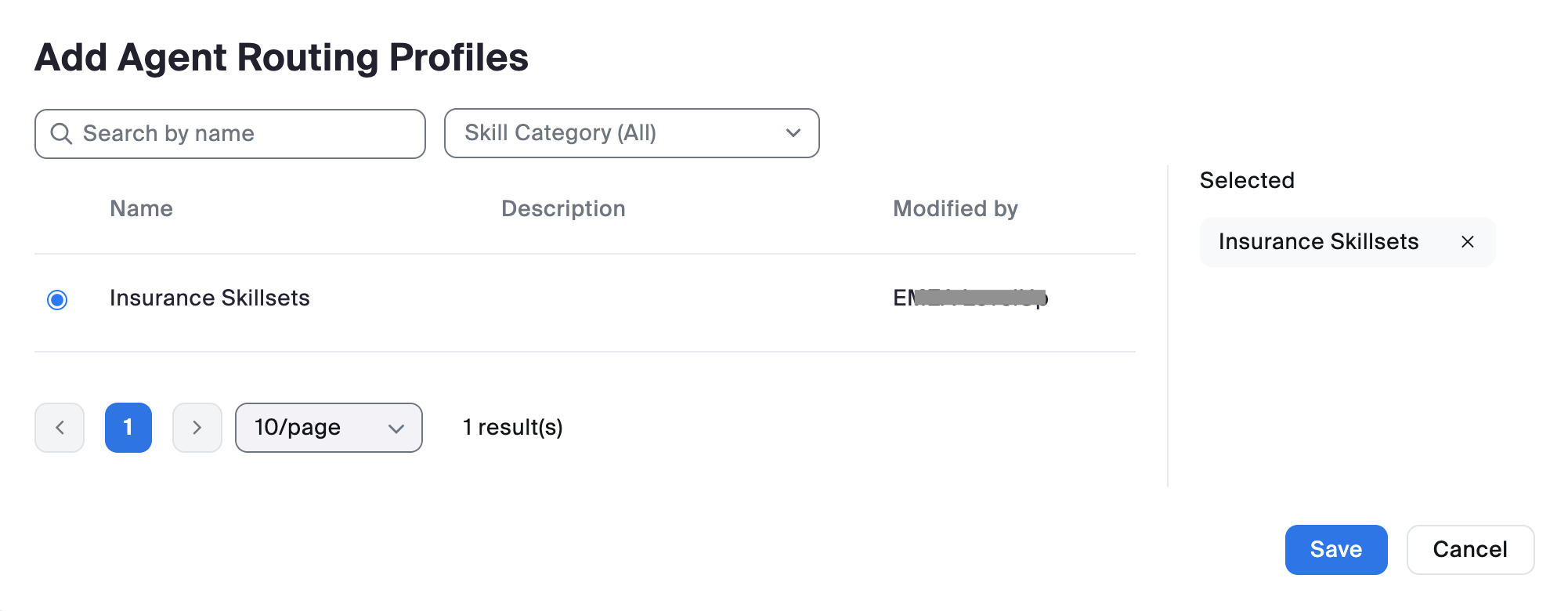
Agent Routing Profiles route engagements to the appropriate agents that can best meet their needs based on previously-created skills. Routing Profiles contain the business requirements of which skill(s) are required and how skills should be factored into the routing of an engagement.
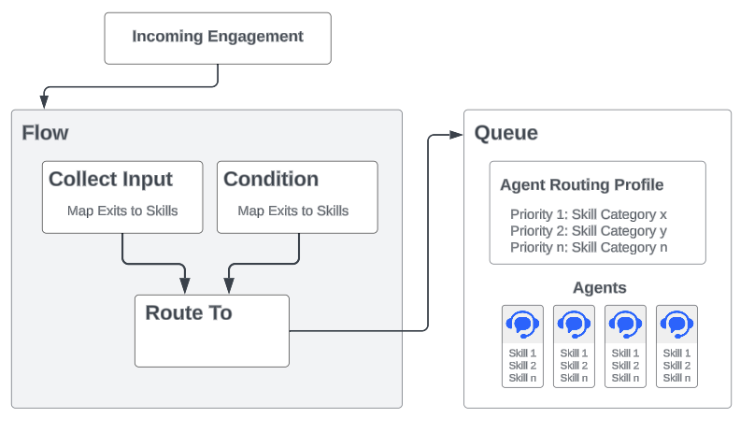
Flows:
Flows are the entry point into the contact centre and provide much of the business logic so a consumer is routed to the right place.
Before the consumer is sent to a queue to be answered by an agent, the flow has the ability to identify what the consumer needs and the necessary skills required of the agent who ultimately answers the engagement.
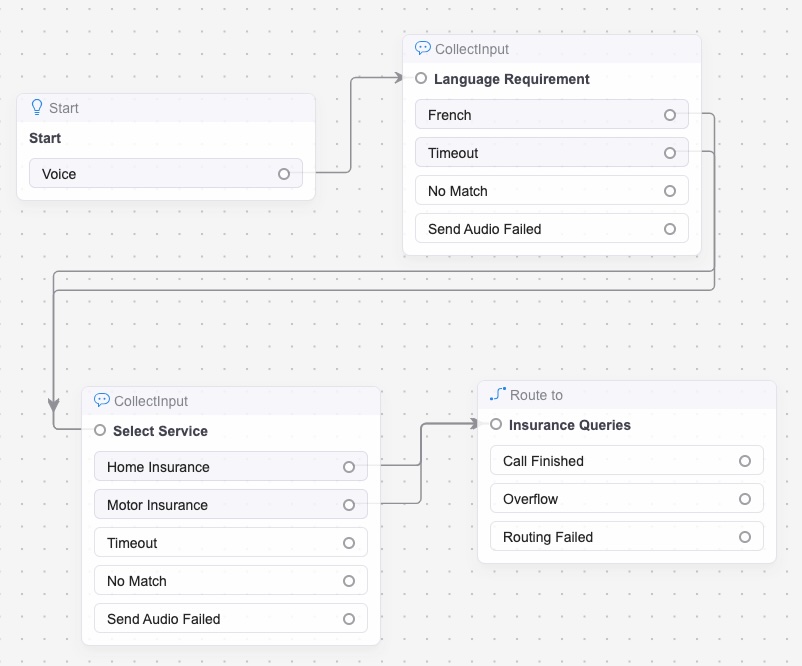
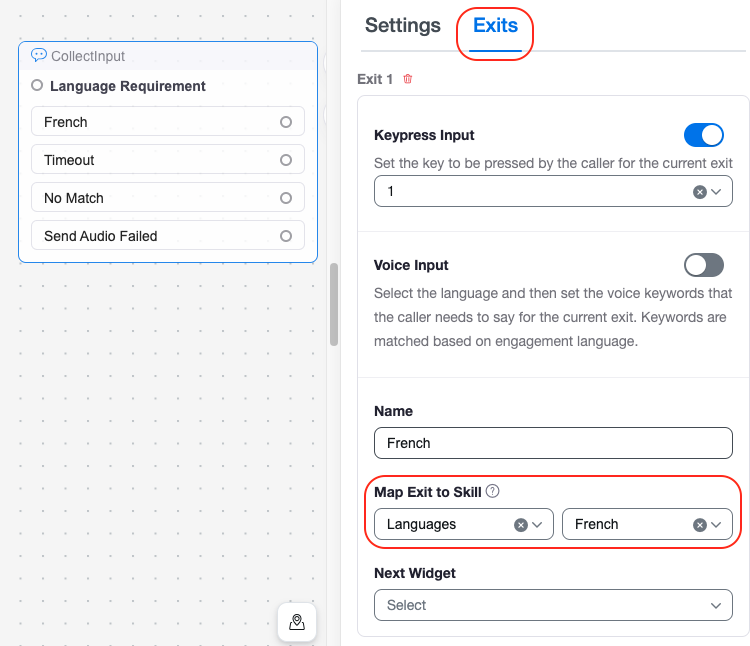
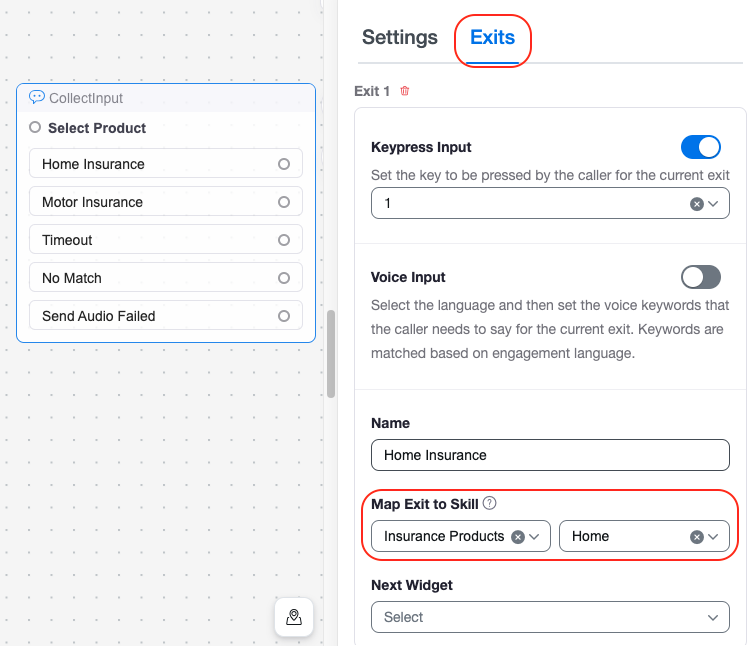
Skills are typically identified using a combination of Collect Input and Condition widgets.
- Collect Input widgets map a skill requirement to consumer input (digit input in an IVR menu, for example).
- Condition widgets map a skill requirement to the contents of a variable.
Once skill requirements have been identified, a Route To widget is used to send the incoming engagement into a queue.
Queues :
Queues manage incoming engagements that need to be distributed to your agents. Agents and Agent Routing Profiles are assigned to queues.